🚀 Given two strings like "listen" and "silent", determine if they contain exactly the same characters in different order (Anagram)
🧩 THE CHALLENGE
Given two strings like "listen" and "silent", determine if they contain exactly the same characters in different order.
Examples:
✅
"listen"↔"silent"→ TRUE✅
"evil"↔"vile"→ TRUE❌
"hello"↔"world"→ FALSE
💡 THE OPTIMAL SOLUTION
Here's the breakthrough algorithm that achieves O(n) time and O(1) space:
public Boolean isAnagram(String s1, String s2) {
int[] frequency = new int[26]; // Fixed array for a-z letters
// Different lengths? Not anagrams!
if (s1.length() != s2.length()) return false;
// Process both strings in ONE loop - O(n)
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) {
frequency[s1.charAt(i) - 'a']++; // Count letters in s1
frequency[s2.charAt(i) - 'a']--; // Subtract letters in s2
}
// If all counters are zero = perfect match!
for (int count : frequency) {
if (count != 0) return false;
}
return true;
}🔬 THE GENIUS BEHIND THE CODE
Character to Index Magic:
'a' - 'a' = 0 → Array position 0
'b' - 'a' = 1 → Array position 1
'l' - 'a' = 11 → Array position 11
'z' - 'a' = 25 → Array position 25The Balancing Algorithm:
Add +1 for each character in string 1
Subtract -1 for each character in string 2
Result = 0 everywhere? → Perfect anagram! ✅
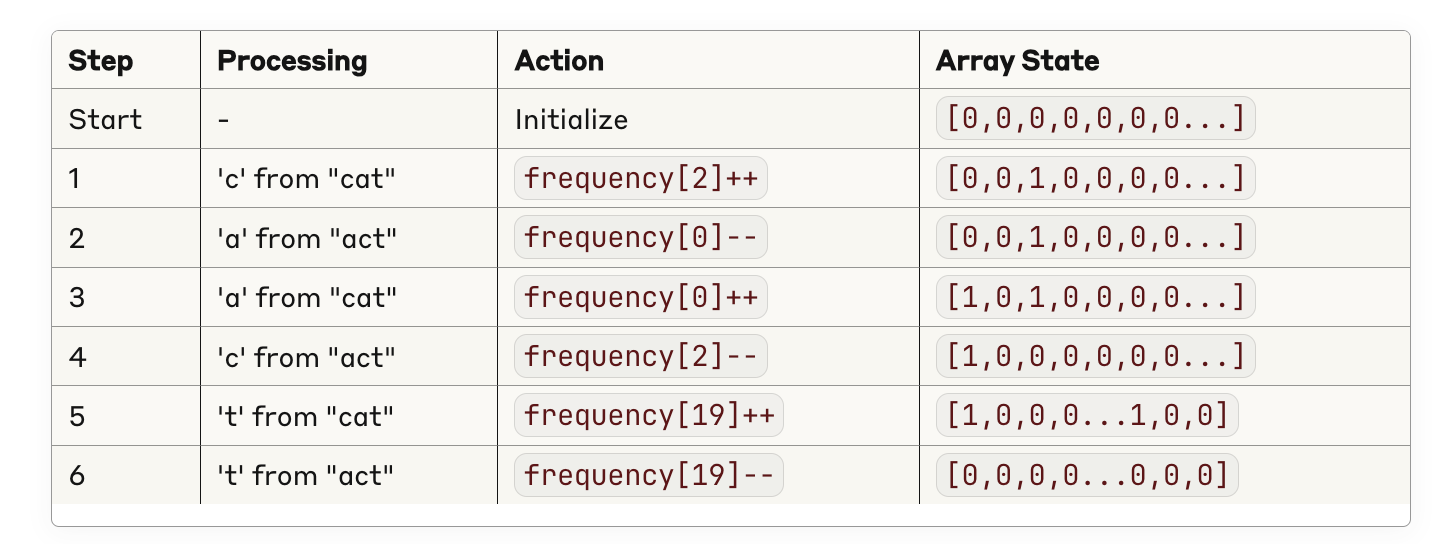
📊 STEP-BY-STEP EXAMPLE: "cat" vs "act"
Final Result: All zeros → ANAGRAM! 🎉
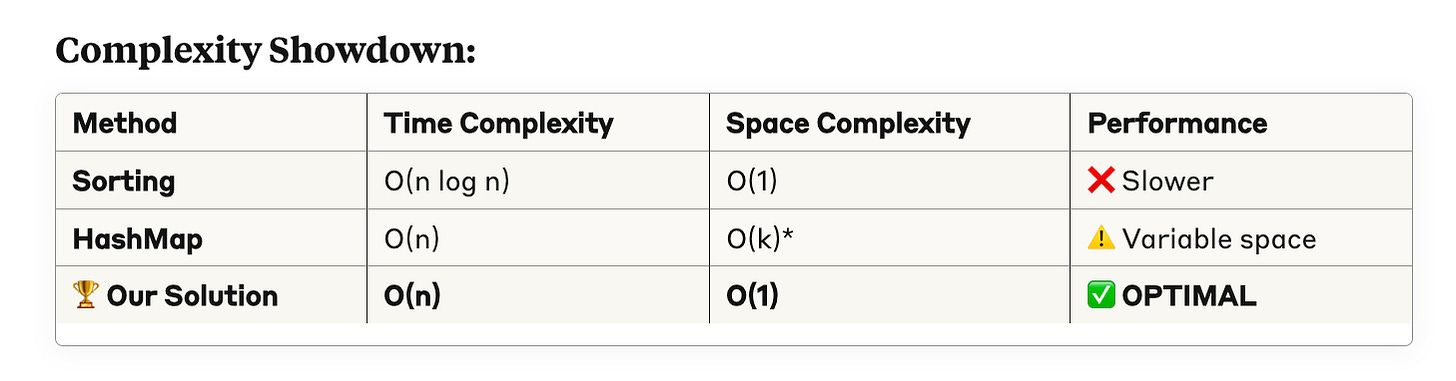
⚡ WHY THIS SOLUTION DOMINATES
*k = number of unique characters
Key Advantages:
🚀 Single pass through both strings
💾 Constant space - only 26 integers
⚡ Cache-friendly - array access beats HashMap
🎯 Theoretically optimal - can't do better than O(n)
🧠 THE ALGORITHM INSIGHTS
✅ Think Arrays Over HashMaps - When dealing with limited character sets
✅ Process Simultaneously - Why make two passes when one suffices?
✅ Character Arithmetic - c - 'a' is a powerful mapping technique
✅ Early Termination - Check length first, save computation
✅ Balance Principle - Add and subtract to detect mismatches